Choosing between analog and digital servos can be confusing. Both types have unique features and uses.
Servos are essential in robotics, RC cars, and planes. Understanding the differences between analog and digital versions is crucial. They control movement and speed in devices. Analog servos respond to signals differently than digital ones. This impacts their performance and application.
In this blog, we will explore the key differences and help you decide which is better for your needs. Knowing these differences can improve your projects and give you more control. Let’s dive in to see how each type works and where they excel.
Introduction To Servos
Servos are devices that control movement in many machines. They are crucial in robotics, RC vehicles, and automation. Understanding how they work helps in choosing the right one for a project.
Analog Vs Digital Basics
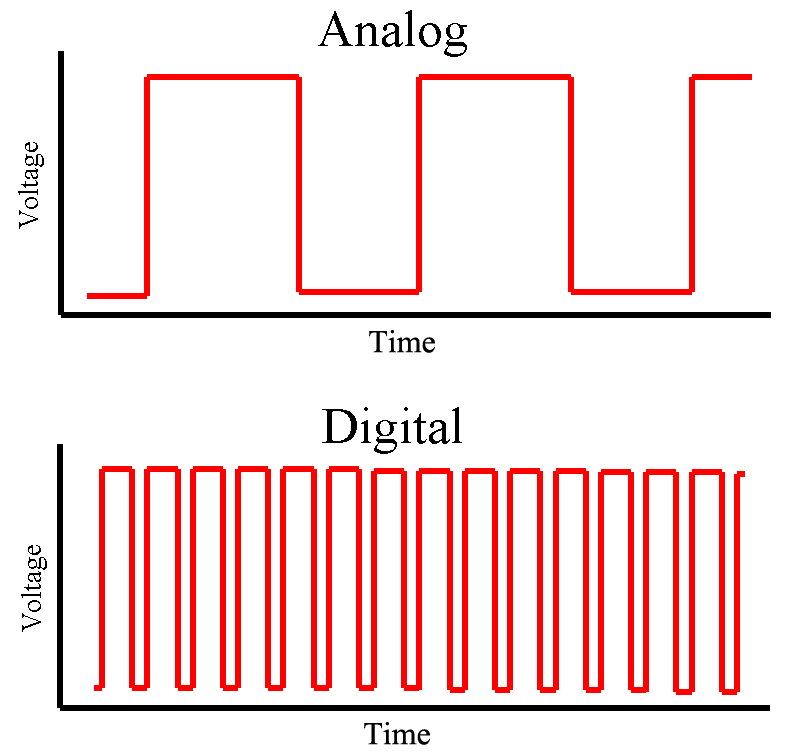
Analog servos receive signals in a continuous wave. Digital servos get signals in pulses. Both types control the motor’s speed and position. The main difference is in the signal processing.
Analog servos process signals slower. They update their position about 50 times per second. Digital servos update much faster, around 300 times per second. This means digital servos react quicker and hold their position better.
Importance In Modern Applications
Servos are vital in many modern technologies. In drones, they control the tilt and direction. Robots use servos for precise movements. RC cars rely on them for steering and speed control.
Choosing the right servo affects performance. For simple tasks, analog servos work fine. For complex tasks, digital servos offer better precision and speed. This makes them ideal for advanced applications.
How Analog Servos Work
Analog servos use a pulse width modulation (PWM) signal to control position. They operate with continuous voltage adjustments. Analog Vs Digital Servo comparison highlights differences in speed and precision.
Analog servos are a vital component in many mechanical systems. They control movements with precision. Understanding their operation helps in various applications.Pulse Modulation
Analog servos receive signals through pulse modulation. These pulses come from a receiver. The length of each pulse determines the servo’s position. Typically, pulses range from 1 to 2 milliseconds. A 1.5-millisecond pulse centers the servo. Shorter or longer pulses move the servo to different angles.Performance Characteristics
Analog servos offer consistent performance. They provide steady torque and speed. Their response time depends on pulse frequency. Higher pulse rates increase responsiveness. Analog servos also have simple electronics. This simplicity makes them reliable. They work efficiently in various conditions. Analog servos are durable and cost-effective. Their performance meets the needs of many projects. “`How Digital Servos Work
Digital servos have become a preferred choice in many applications due to their precision and reliability. Unlike analog servos, digital servos use advanced technology to control movements. This technology allows them to offer faster and more accurate responses.
Digital servos are equipped with a microprocessor. This microprocessor processes the incoming signals and adjusts the motor accordingly. This leads to smoother and more efficient operations.
Signal Processing
Digital servos process signals differently than analog servos. They use a microprocessor to interpret the signals. This microprocessor receives the signals from the transmitter and converts them into commands for the motor.
The microprocessor sends high-frequency pulses to the motor. These pulses result in quicker and more precise movements. The high-frequency pulses reduce the delay between the signal and the action.
In analog servos, the signal is continuous and less precise. Digital servos use pulse-width modulation (PWM) for better control. PWM allows the servo to adjust the motor speed and position accurately.
Advanced Features
Digital servos come with advanced features that enhance their performance. They offer programmable settings, allowing users to customize their operations. Users can adjust the servo’s speed, torque, and direction.
Many digital servos have built-in fail-safes. These fail-safes protect the servo from damage if it receives incorrect signals. Some servos also have feedback systems. Feedback systems monitor the servo’s position and ensure it matches the input commands.
Digital servos often have higher resolution than analog servos. Higher resolution means more precise control over movements. This precision is crucial in applications requiring accurate positioning.
Another feature is the ability to handle higher loads. Digital servos can manage heavier weights without compromising performance. This makes them suitable for demanding applications like robotics and industrial machinery.

Credit: www.radiocontrolinfo.com
Performance Comparison
When comparing analog and digital servos, performance is a key aspect. Understanding their speed, precision, torque, and holding power can help you decide which is better for your needs.
Speed And Precision
Digital servos offer faster response times. They receive signals more quickly, resulting in precise movements. Analog servos are slower. They have a delay in signal processing. This makes digital servos ideal for tasks that require high accuracy.
Torque And Holding Power
Torque is the turning force of a servo. Digital servos generally provide higher torque. They can maintain this power consistently. Analog servos may struggle under heavy loads. Digital servos also excel in holding power. They maintain positions firmly. Analog servos may wobble under pressure. This makes digital servos reliable for demanding applications.
Energy Efficiency
In the world of servos, energy efficiency is a key factor. Analog and digital servos both have their strengths and weaknesses. Understanding their energy efficiency can help you make the right choice.
Power Consumption
Analog servos consume power continuously. They constantly adjust to maintain their position. This can lead to higher energy usage over time.
Digital servos, on the other hand, use power more efficiently. They make rapid adjustments only when needed. This results in lower overall power consumption.
Heat Generation
Analog servos generate more heat. Continuous adjustments create more friction and heat. This can affect performance and longevity.
Digital servos produce less heat. They work in short bursts, reducing friction. Less heat means better performance and longer life.
Credit: www.radiocontrolinfo.com
Durability And Reliability
When choosing between analog and digital servos, durability and reliability play a big role. Both types have their advantages, but understanding their differences can help you make the right decision.
Component Lifespan
Analog servos use simple components. These components often last a long time. They are less likely to break down under normal use. Many users find analog servos reliable for this reason.
Digital servos, on the other hand, use advanced technology. This technology offers better performance. But, the advanced components may wear out faster. Digital servos may need more frequent maintenance and replacement.
Failure Rates
Failure rates are an important aspect of reliability. Analog servos have a lower failure rate. Their simpler design means fewer things can go wrong. Users trust analog servos for long-term projects.
Digital servos can be more prone to failure. The high-tech components are more sensitive. Digital servos may fail if not maintained properly. Regular checks are important for ensuring their reliability.
Cost Considerations
Choosing between analog and digital servo motors involves many factors. One of the most important is cost. Understanding the cost considerations can help you make an informed decision. This section breaks down the initial investment and long-term value of both types.
Initial Investment
Analog servos are usually less expensive upfront. They are simpler in design and manufacturing. This makes them a cost-effective choice for budget-conscious buyers. Digital servos, on the other hand, come at a higher initial cost. They offer advanced features and better performance. The extra cost reflects their enhanced capabilities.
For those with tight budgets, analog servos may seem more appealing. But it’s essential to consider the overall value. Initial savings might be tempting, but it’s crucial to weigh all factors. Think about how each type fits into your long-term plans.
Long-term Value
Analog servos, while cheaper initially, may cost more in the long run. They can wear out faster and need more frequent replacements. Maintenance costs can add up over time. Digital servos are more durable and reliable. Their advanced technology reduces wear and tear.
Over time, digital servos can save money. They last longer and perform better. This means fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs. Investing more upfront in digital servos can lead to greater savings. For those looking for long-term solutions, digital servos offer better value.
Best Use Cases
Analog servos excel in applications requiring smooth and precise movements, such as robotics and model airplanes. Digital servos offer faster response times and are ideal for tasks needing high accuracy, like drone flight controls and RC cars.
Best Use CasesChoosing between analog and digital servos can be tricky. Each has its strengths and is better suited for different applications. Let’s break down the best use cases for both types of servos.Analog Servo Applications
Analog servos are reliable and cost-effective. They are perfect for beginners and hobbyists.You’ll find them in RC cars, boats, and planes. Their simplicity makes them easy to control and maintain.Analog servos are also great for basic robotics. If you’re building a simple robot or mechanical arm, they can handle the job without breaking the bank.Digital Servo Applications
Digital servos excel in precision and speed. They are ideal for tasks requiring high accuracy.In competitive RC activities, digital servos provide the edge needed. They respond quicker and hold positions better than analog servos.Digital servos are also used in advanced robotics. If you’re working on a project that requires precise movements, like a robotic arm used in surgery, digital is the way to go.What kind of projects are you working on? Knowing the strengths of each servo type can help you choose the right one for your needs.
Credit: www.linkedin.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Digital Or Analog Servos Better?
Digital servos offer faster response times and more precision. Analog servos are typically cheaper and simpler. Choose based on your specific needs.
How Do I Know If My Servo Is Analog Or Digital?
Check the label or datasheet for specifications. Analog servos use PWM signals, digital servos use high-frequency pulses.
What Is The Advantage Of A Digital Servo?
A digital servo offers precise control, faster response, and higher torque. It improves accuracy and performance in various applications.
Can I Mix Digital And Analog Servos?
Yes, you can mix digital and analog servos. Ensure they are compatible with your receiver and power supply. This combination can offer flexibility in your setup.
What Is The Difference Between Analog And Digital Servo?
Analog servos use continuous signals, while digital servos use high-frequency pulses. Digital servos offer faster response and precision.
Conclusion
Choosing between analog and digital servos depends on your specific needs. Digital servos offer quick responses and precision. Analog servos are more affordable and simpler. Both have their strengths. Evaluate your project to decide. Consider your budget and requirements. Make an informed choice for best results.
Both types can serve you well. Happy building!






